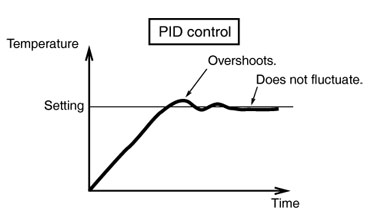
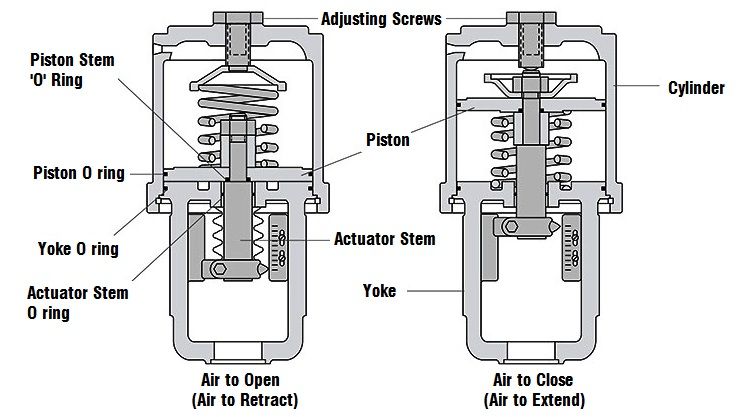
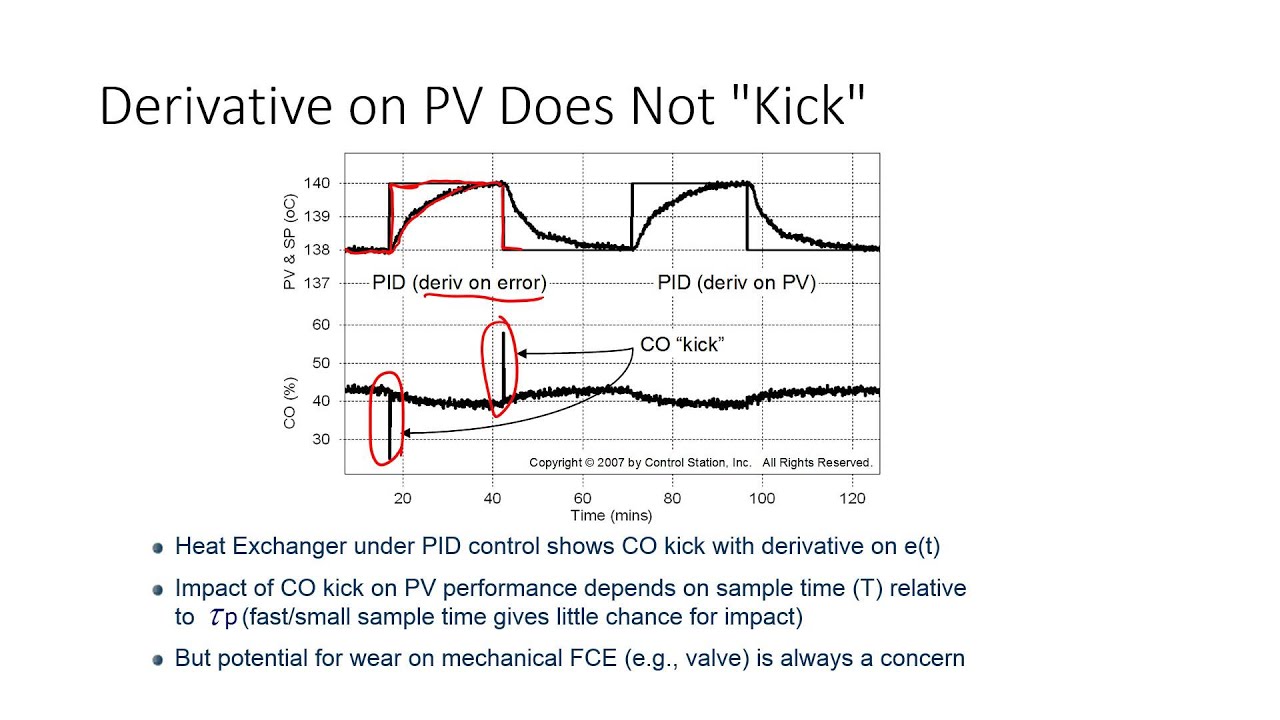
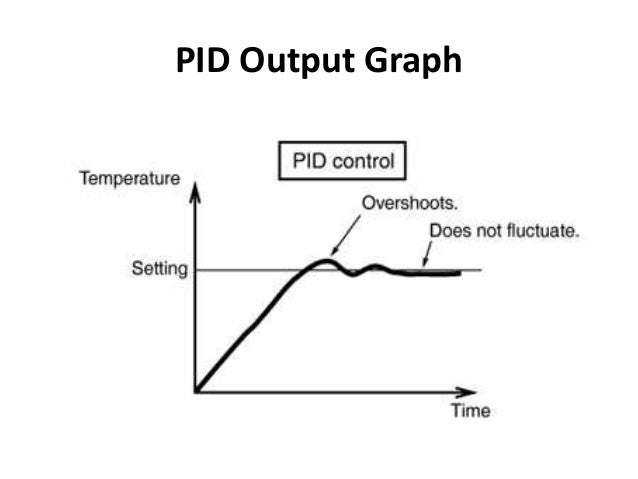
Pid Control Valve Adjustment
Pid stands for three variables that make up the control algorithm.
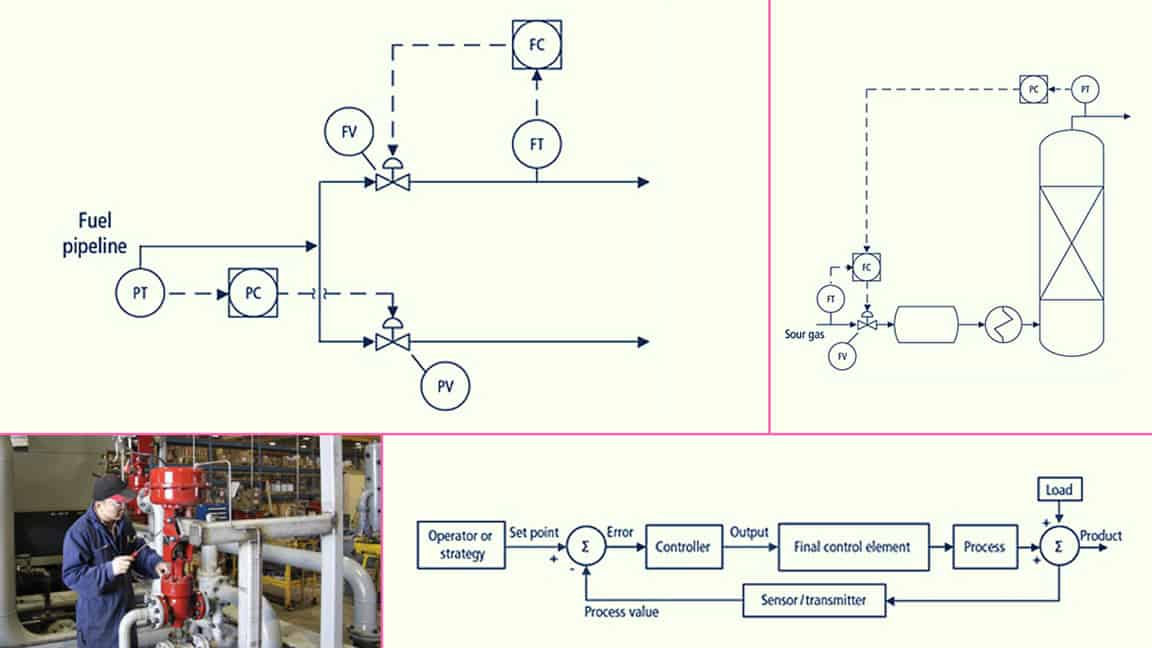
Pid control valve adjustment. A pid control loop is a critical function within many industrial processes. Although this concept has a very extensive control systems background theory we ve come to a point where we can utilize a plc based instruction to control the system without worrying about all the details. Achieving responsive and stable valve control with pid tuning by alyssa jenkins whether you are giving your new alicat mass flow controller a setpoint for the first time or putting a trusted alicat pressure controller into a new system your device sometimes may need a few adjustments to achieve the highest degree of control stability. Op output a signal to a device that can change the pv.
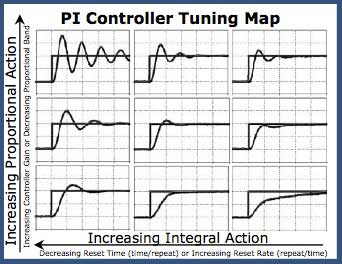
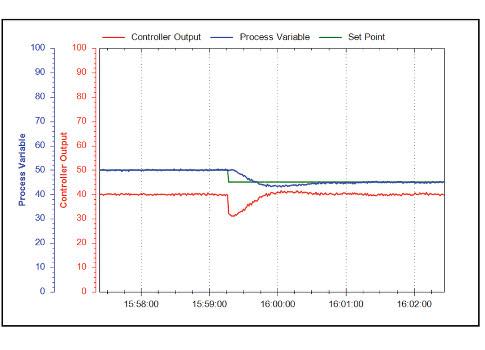
A mechanical flow controller manipulates the valve to maintain the downstream flow rate in spite of the leakage. It gives an engineer the ability to control a certain process based on the feedback received from field devices. Continuous control before pid controllers were fully understood and implemented has one of its origins in the centrifugal governor which uses rotating weights to control a process this had been invented by christiaan huygens in the 17th century to regulate the gap between millstones in windmills depending on the speed of rotation and thereby compensate for the variable speed of. Increase the integral gain in small increments and with each adjustment change the set point to see how the controller reacts.
Pid proportional integral derivative algorithm this is not a p id which is a piping or process and instrumentation diagram. For example a tank level pid loop might have an op in k h flow rather than to a valve. Pv process variable a quantity used as a feedback typically measured by an instrument also sometimes called mv measured value. Time proportioning varies the on time of relay triac and logic outputs to deliver a variable output power between 0 and 100.
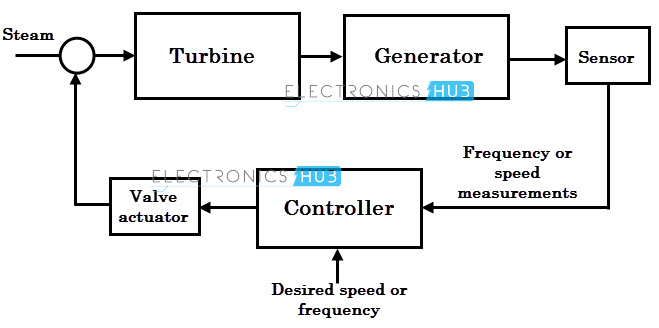
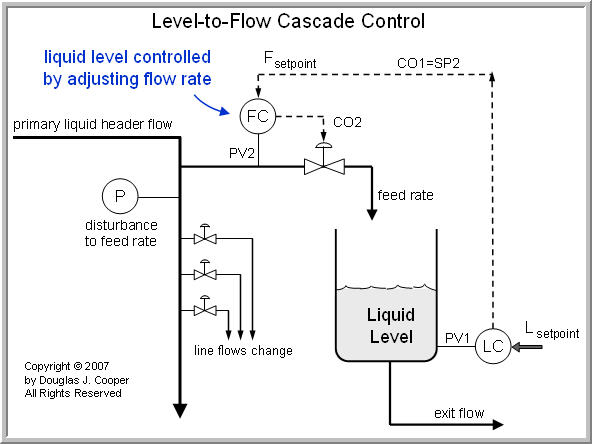
The basic pid cascade is a pair of pid loops where the op of the master primary loop sets the sp of the slave secondary loop. That master op is sent to the sp of a slave pid loop controlling flow. Proportional integral and derivative. The size of the valve opening at time t is v t the flowrate is measured by the vertical position of the float f t the gain of the controller is a b this arrangement would be entirely impractical for a modern flow control application but a similar principle was actually used in.
To obtain straight line temperature control a pid controller requires some means of varying the power smoothly between 0 and 100. Always start with small steps when adjusting a pid controller and give time between each adjustment to see how the controller reacts.